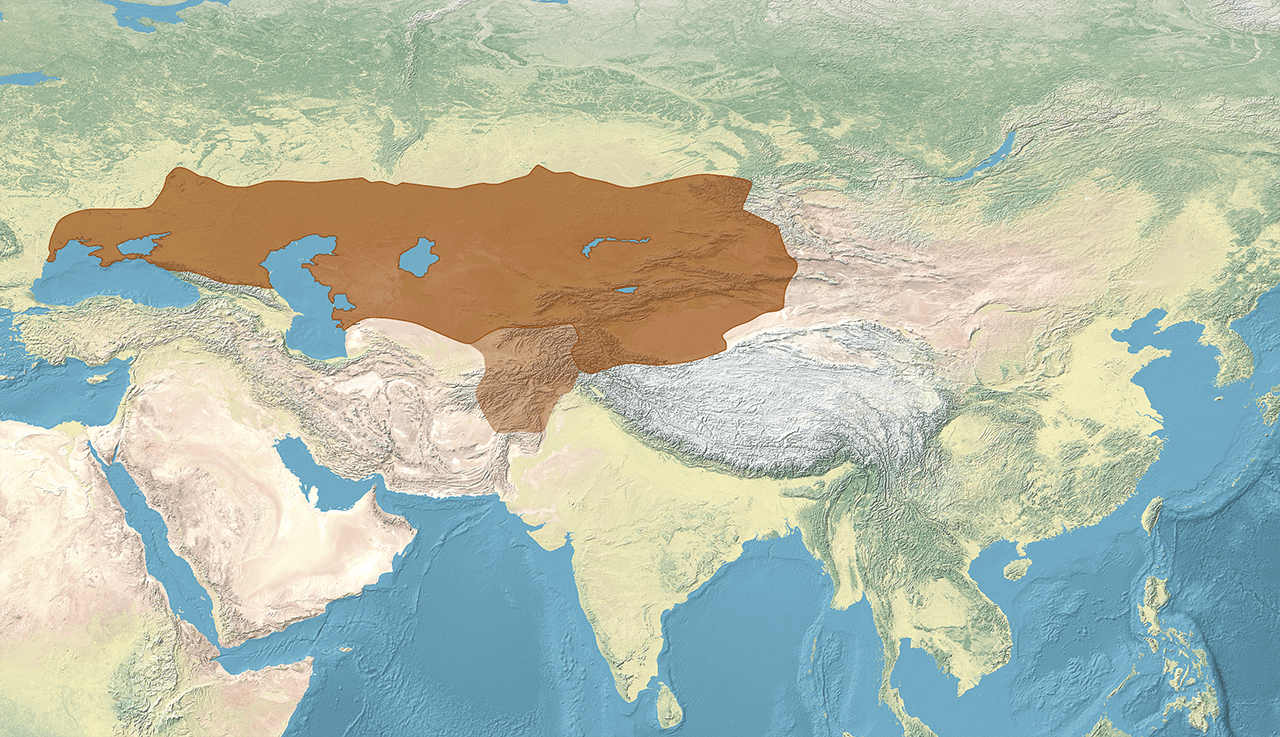
Western Turks
The Western Turkic Khaganate (Chinese: 西突厥; pinyin: Xī Tūjué) or Onoq Khaganate, was a Turkic khaganate in Eurasia, which formed as a result of the wars during the beginning of the 7th century (593–603) after the First Turkic Khaganate, which was founded in the 6th century on the Mongolian Plateau by the Ashina clan, split into a western and eastern khaganate.
The confederation as a whole was called Onoq, meaning "ten arrows". According to a Chinese source, the Western Turks were organized into ten divisions.
The khaganate's capitals were Navekat, the summer capital and Suyab, which was the principal capital, both situated in the Chui River valley in Kyrgyzstan, to the east of Bishkek. Tong Yabgu's summer capital was near Tashkent and his winter capital Suyab.
The Eastern Turkic Khaganate was subjugated by the Tang dynasty in 657 and continued as its vassal, before finally collapsing in 742. In the west, the breakup of the Western Turkic Khaganate led to the rise of the Turkic Khazar Khaganate (c. 650–969).
What You'll Get
Western Turks
The Western Turkic Khaganate (Chinese: 西突厥; pinyin: Xī Tūjué) or O…
Yue Jue Shu
Yuejueshu 越絕書 "End of the kingdom of Yue" is a history of …
Sancai
Sancai (Chinese: 三彩; pinyin: sāncǎi) is a versatile type of decorat…
Yangtze River
The Yangtze River, Yangzi River or Chang Jiang (simplified Chinese: 长江…
Xianbei
The Xianbei (simplified Chinese: 鲜卑; pinyin: Xiānbēi) were an ancie…
Woodblock printing
Woodblock printing or block printing is a technique for printing text, …
Pipa
The pipa (Chinese: 琵琶; pinyin: pípá) is a traditional Chinese musical…
Silk Road
The Silk Road derives its name from the highly lucrative trade of silk …
Chang'an
Chang'an, located in China's Shaanxi Province, was the capital city of …
