Silk Road
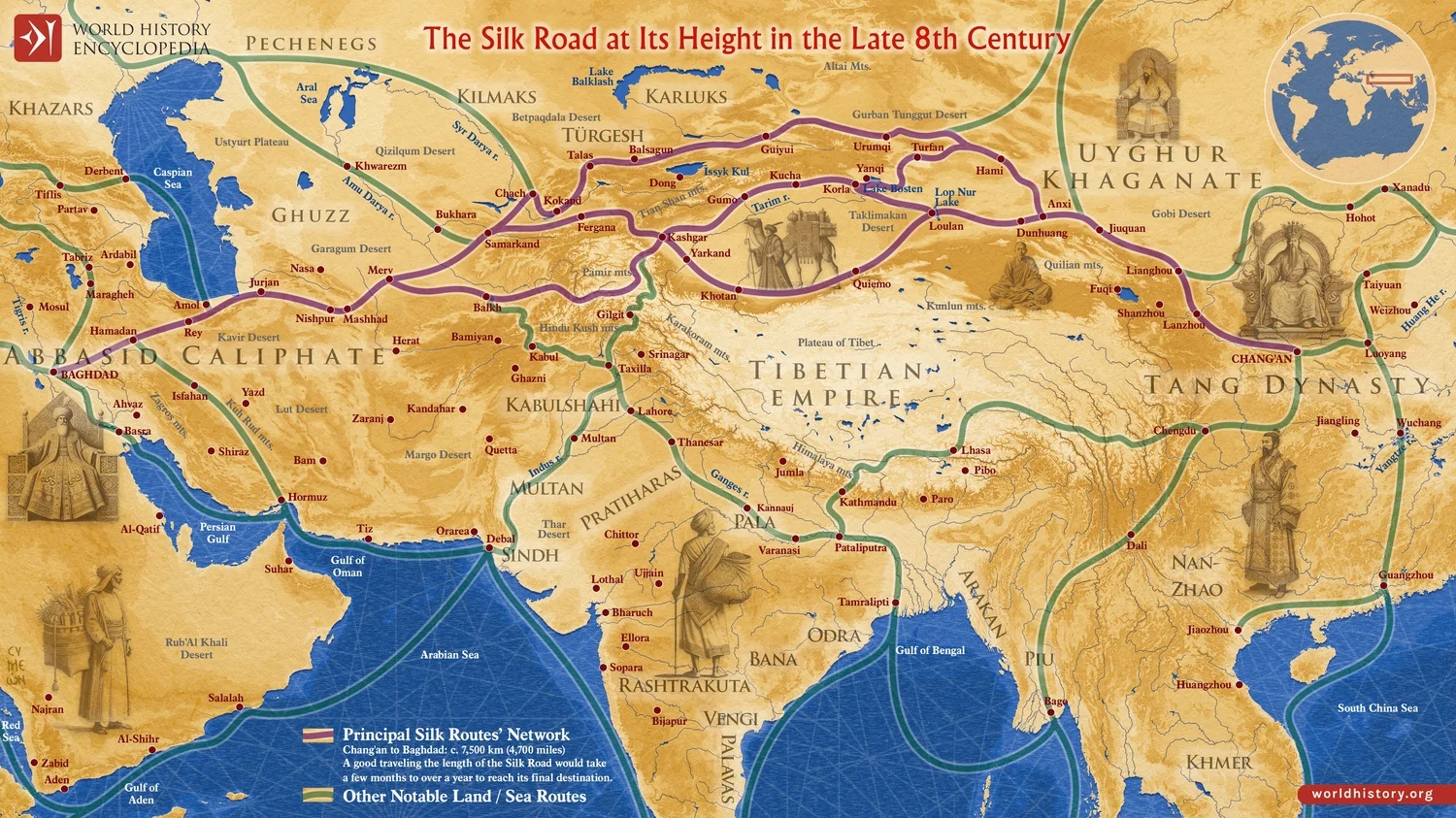
The Silk Road derives its name from the highly lucrative trade of silk textiles that were primarily produced in China. The network began with the expansion of the Han dynasty (202 BCE – 220 CE) into Central Asia around 114 BCE, through the missions and explorations of the Chinese imperial envoy Zhang Qian, which brought the region under unified control. The Chinese took great interest in the security of their trade products, and extended the Great Wall of China to ensure the protection of the trade route. The Parthian Empire provided a vital bridge connecting the network to the Mediterranean. Meanwhile, the rise of the Roman Empire in the west further established the western terminus of the interconnected trade system. By the first century CE, Chinese silk was widely sought after in Rome, Egypt, and Greece. Other lucrative commodities from the East included tea, dyes, perfumes, and porcelain; among Western exports were horses, camels, honey, wine, and gold. Aside from generating substantial wealth for emerging mercantile classes, the proliferation of goods such as paper and gunpowder greatly affected the trajectory of political history in several theatres in Eurasia and beyond.
What You'll Get
Western Turks
The Western Turkic Khaganate (Chinese: 西突厥; pinyin: Xī Tūjué) or O…
Yue Jue Shu
Yuejueshu 越絕書 "End of the kingdom of Yue" is a history of …
Sancai
Sancai (Chinese: 三彩; pinyin: sāncǎi) is a versatile type of decorat…
Yangtze River
The Yangtze River, Yangzi River or Chang Jiang (simplified Chinese: 长江…
Xianbei
The Xianbei (simplified Chinese: 鲜卑; pinyin: Xiānbēi) were an ancie…
Woodblock printing
Woodblock printing or block printing is a technique for printing text, …
Pipa
The pipa (Chinese: 琵琶; pinyin: pípá) is a traditional Chinese musical…
Silk Road
The Silk Road derives its name from the highly lucrative trade of silk …
Chang'an
Chang'an, located in China's Shaanxi Province, was the capital city of …
